Onkos kukaan tutustunut tarkemmin noihin Ruotsalaisten/Tanskalaisten yritysten optioihin? Siellä tuntuu useammalla pikkufirmalla olevan optio-ohjelmia. Varsinkin kahden Tanskalaisen yrityksen optiot pisti silmään. Curasightin option hinta nyt 8 kr ja optiolla saa merkitä syksyllä osaketta hintaan 17.2kr, mutta osakekurssi 27,9kr. Cessatechin option hinta taas 6,3kr ja optiolla saa merkitä loppuvuonna osaketta hintaan 10kr. Osakkeen hinta nyt 21kr. Jos oon oikein ymmärtänyt, niin joko osakekurssin tai optioiden hinta on pahasti väärässä. Varsinkin kun ottaa huomioon, että kumpikin on lääkealan alkuvaiheen yritys, joten optioilla tulisi olla kohtalaisesti myös aika-arvoa…
Optioilla normi riskipreemio sille että ei ole mitään takeita mitä se osake on loppuvuonna. Hinta lähestyy osakkeen hintaa (+merkintähinta) sitä mukaa kun merkintäpäivä lähestyy.
Hinta alempi = löytyy myyjiä jotka haluaa rahat nyt eikä loppuvuonna ja on valmis tästä ottamaan nimellisesti tappiota.
High-speed trading firms are paying brokers bil-lions of dollars a year to execute options orders, leading them to promote the risky trades whose popularity has boomed among small investors.
The practice, called payment for order flow, has made options a cash cow for brokerages such as Robinhood Markets Inc. and TD Ameritrade. They can make twice as much or more from selling cus-tomers’ options orders as they do from selling order flow for stocks.
In the 12 months through June, the 11 largest U.S. retail brokerages col-lected $2.2 billion for selling customers’ options orders, according to Larry Tabb, head of market-structure research at Bloomberg Intelligence. That was about 60% higher than their take from selling equities orders.
During that period, major brokers were paid an average of about 16 cents for each 100 shares of their customers’ stock orders, compared with about 54 cents for equiva-lent-sized options orders, Mr. Tabb’s data show.
While the payments are legal and have existed for decades, they came under renewed scrutiny after the January trading frenzy in shares of Game-Stop Corp. The Securities and Ex-change Commission is reviewing payment for order flow, and its chair-man, Gary Gensler, has said the agency is open to banning the practice.
Critics say payment for order flow has reshaped brokers’ business models to make them intent on juicing more trading activity from customers, sometimes through gamelike smartphone apps. Some warn that larger order-flow pay-ments from options activity can effectively push inexperienced customers into risky trades they don’t under-stand, exposing them to large potential losses.
Ilmeisesti myös jenkki optioiden tappiot voi vähentää verotuksessa yksityishenkilönä?
Tässä Nasdaqin artikkelissa todetaan, että Nokian 23.12.2021 optiot eivät todennäköisesti ole erääntyessään ”on the money”,
December 23rd Options Now Available For Nokia
Contributor
Nov 4, 2021 11:49AM EDT
Turning to the calls side of the option chain, the call contract at the $7.50 strike price has a current bid of 2 cents. If an investor was to purchase shares of NOK stock at the current price level of $5.69/share, and then sell-to-open that call contract as a “covered call,” they are committing to sell the stock at $7.50.
Considering the call seller will also collect the premium, that would drive a total return (excluding dividends, if any) of 32.16% if the stock gets called away at the December 23rd expiration (before broker commissions).
Of course, a lot of upside could potentially be left on the table if NOK shares really soar, which is why looking at the trailing twelve month trading history for Nokia Corp, as well as studying the business fundamentals becomes important.
Below is a chart showing NOK’s trailing twelve month trading history, with the $7.50 strike highlighted in red:
Considering the fact that the $7.50 strike represents an approximate 32% premium to the current trading price of the stock (in other words it is out-of-the-money by that percentage), there is also the possibility that the covered call contract would expire worthless, in which case the investor would keep both their shares of stock and the premium collected. The current analytical data (including greeks and implied greeks) suggest the current odds of that happening are 99%
On our website under the contract detail page for this contract, Stock Options Channel will track those odds over time to see how they change and publish a chart of those numbers (the trading history of the option contract will also be charted). Should the covered call contract expire worthless, the premium would represent a 0.35% boost of extra return to the investor, or 2.62% annualized, which we refer to as the YieldBoost.
Jenkkien ETF:iä ei pysty Suomessa ostamaan, mutta pystyykö näiden ETF:ien optioita?
Tässä hyvä long call-optioiden laskuri…
Mistä tai minkä välittäjän kautta ostatte optioita
Mandatum trader go, jolla pääsee hyvin USAn markkinoille.
Lasketaanko warranttin stop loss päätöskurssista vai riittääkö, että osake on käynyt tason alla edellisenä päivänä. Esimerkkinä Teslan long-warrantti. Stop loss 900$, kurssi päivä alkaessa ja loppuessa yli 900$. Kurssi kuitenkin käynyt alle 900$ illala kun euro tuotteella ei ole edes voinut käydä kauppaa. Tapahtuuko knock-out?
Tuo on kerrottu kyseisen johdannaisen tuotetiedoissa - varma tieto on oltava oleellisista ominaisuuksista.
Option Type Call
American Exercise Type
Exercise Time is 11:00 a.m. (Helsinki time)Reference Price shall mean the closing price of the Underlying determined and
published by the Reference Agent on the Valuation Date.For the purpose of determining whether the Observation Price touches or falls below
the Current Knock-Out Barrier, each determination of the price of the Underlying by the
Reference Agent during the Observation Period shall be relevant.
Nämä lienee oleelliset kohdat dokumentissa. Onpa hankalaa kapulakieltä. Sain käsityksen, että edellisen päivän päätöskurssin mukaan tarkistetaan seuraavana päivänä tälläinen nordnetin turbowarrantti. Jolloin päätöskurssin ollessa ylempi kuin stop loss tuote ei knockaannu vaikka hinta olisi käynyt alle. Voin olla myös väärässä.
Interactive brokers. Kattava ja toimiva myös hifistelijälle, mm. automatisoidut optiosrategiat, jne.
Sure, they probably know, or can easily learn, the basics: puts and calls; in-the-money and out-of-the money; HV (historic volatility) and IV (implied volatility); the naked and the spread.
But what about Vomma……
If the term vomma is Greek to you, that is because it literally is. Options traders use various Greek letters and terms to describe the sensitivity of an option’s price to various factors, such as volatility in the underlying security. The most basic terms—delta, gamma, theta, vega, and rho—are referred to as “major Greeks.
” Vomma, on the other hand, is known as a minor Greek because it provides insight into vega.
Delta is a ratio that mea-sures how much an option’s price is expected to change for every $1 shift in the price of the underlying security. Deltas on puts (which give the owner the right to sell a security at a certain price) can range from 0 to negative 1; on calls (which give the owner the right to buy a security at a certain price) they are 0 to positive 1. If a call has a delta of 0.50 and the price of the underlying stock rises $1, the price of the call will go up, theoreti-cally, about 50 cents, as long as every thing else remains constant.
Delta can offer a rough gauge on the odds an option will wind up in the money at expiration. (A call option is in the money if the market price is above the strike price; a put option is in the money if the market price is below the strike price.) For example, a trader buying a far out-of-the-money put with a negative 0.05 delta has a 5% chance of the option expiring in the money. Not a good bet.
Delta neutral is a common phrase. It means a combina-tion of option deltas add up to zero, and the combined options will move, for a time, 100% in lockstep with the underlying stock. It’s very useful for hedging a stock’s movement.
Gamma This one is tougher; it measures the rate of change in the delta of an option for every one-point move in the price of the underlying security. What does this mean? An oft-used analogy is that delta is an option’s speed, and gamma reflects acceleration, a nuance that may be more important to professional traders hedg-ing large portfolios.
Gamma is small when an option is deep in or out of the money. It is at its largest when the option is near or at the money.
Retail traders may often hear advanced traders mention gamma scalping, which is, very broadly speaking, adjusting an options position frequently with a primary goal of not losing money due to theta (see below).
Theta measures the rate of change in an option’s value due to time, and is usually expressed as a negative. For example, if an option’s theta is minus 0.20, an investor can expect its premium to decline, or decay, 20 cents a day, if everything else remains constant. The rate of decay tends to accelerate as the option nears expira-tion.
Option writers, or sellers, collect theta when they open a trade, by receiving a small cash payment, a premium, for the risk they are taking on the trade, not unlike how insurance firms collect premiums.
Vega, which isn’t a Greek letter but one of the Greeks, nonetheless, measures an option’s price sensitivity—how much it could change—in response to implied volatility changes in the underlying security. Vega is a higher number for long-dated options than for those expiring soon; long posi-tions will be positive, however, and short posi-tions will be negative.Vega is useful for hedging against implied-volatility changes; changes in vega are mea-sured by the aforemen-tioned vomma, a minor Greek, (a Pyrrho not a Plato, you might say).
Perhaps more useful is this trader’s tip: If the vega is smaller than the option’s bid-ask spread, then the spread isn’t competitive.
RHO This comes in last, and for good reason. It measures the expected change in an option’s price for every one-percentage-point change in interest rates. Considering interest rates have pretty much disappeared, no one tracks it these days. [tilanne on alkanut muuttua 2/2022].
The above is intended to show new traders how much they may not know about the art and science of options trading, a type of investment (sort of) where smart people sometimes get wiped out (and mint mil-lions).
Löysinpä selkeän esityksen erilaisista optiostrategioista. Kuinka suuren osan noista muistaa ulkoa?
Vastaan omaan vanhaan kysymykseeni, että kyllä pystyy. Periaatteessa näin pystyy myös hankkimaan jenkki-etf:iä, kun lunastaa erääntymisen yhteydessä.
Vastaan nyt vähän vanhaan ketjuun kun tähän törmäsin.
Noissahan ei sinänsä ole mitään muistamista. Optioista ei kannata suotta tehdä liian monimutkaisia itselleen. Eurooppalainen optio on lopulta varsin yksinkertainen tuote (ja amerikkalaisen payout on maturiteetissa sama).
Jos miettii ihan sitä että mikä on option arvo maturiteetissa, niin sehän tulee ihan kaavasta (ostaessa) max(0, S-K) call option tapauksessa, ja kaavasta max(0,K-S) putin tapauksessa. Tässä S siis osakkeen hinta ja K on strike. Myydessä lisää vain miinusmerkin. Kaikki nuo strategiat tuossa linkissä on vain summia näistä funktiosta lukuunottamatta niitä joissa on useamman maturiteetin optioita. Oikeastaan mielenkiintoisesti voidaan mikä tahansa eurooppalainen optio jonka payoff on jokin konveksi funktio h: R->R (tai voidaan esittää konveksien funktioiden konbinaationa) ostamalla ja myymällä tarpeaksi useaa eri optiota oikeilla painoilla (Carr-Madan). Näin voidaan esimerkiksi replikoida volatiliteetti johdannaisia markkinoilla myytävillä eurooppalaisilla vanilla optioilla.
Itse tosin pysyttelen kaukana osake optioista. Liikaa vipua ja pitäisi olla jotain mieltä osakkeiden liikkeistä. Se on vaikeaa tai liki mahdotonta. ![]()
Avaatko nyt vähän enemmän mitä tarkoitat tuolla lauseella? Tai miten se pätee amerikkalaisiin optiohin?
Tietysti jos ei halua tehdä sijoittamisesta monimutkaisempaa, niin kannattaa varmaan yleensä pysyä erossa optiosta. ![]()
En ole oikein törmännyt keskusteluun johdolle jaettavista ilmaisista tai puoli-ilmaista osakkeista. Omistan esim. Constia, koska se tuntuu halvalta. Nyt kuitenkin alkoi kylmätä kun katsoin heidän optio-ohjelmaa. Vuonna 2020 jaettiin 245 000 osaketta ilmaiseksi ja tänä vuonna 250 000 osaketta ilmaiseksi johdolle. Myös näyttää löytyvän satunnaisia palkkioita vähän sieltä ja täältä.
https://otp.tools.investis.com/clients/fi/consti/omx/omx-story.aspx?cid=1257&newsid=70749&culture=fi-FI
https://otp.tools.investis.com/clients/fi/consti/omx/omx-story.aspx?cid=1257&newsid=74565&culture=fi-FI
Pyöreästi on 0,5miljoonaa osaketta jaettu sijoittajan näkökulmasta tuhkana tuuleen.
7 858 267 on osakkeiden kokonaismäärä Constin sivujen mukaan, joten noin 7 358 000 oli ennen. Tuo lisäys on iso prosentuaalisesti. Muutamassa vuodessa sijoittajat on menettänyt noin 6,8% optio-ohjelman takia jos tätä oikein tulkitsen ((7 858 267)/(7 358 000) -1 = 0,068 ->6,8%. Valitettavasti näen tässä kaavan, joka jatkuessa on täysin tuhoisa itselleni. Johtohan nauttii tietenkin tällaisesta, mutta tämä ei voi olla hyvä kurssin kehitykselle. Enkä usko että se luo yhtään lisäarvoa.
Henkilöstölle jaettavat optiot on mielestäni ihan hyvä idea kun sillä saadaan työntekijät sitoutettua ja motivoitua. Johto on monesti itsekin niitä suuromistajia, joten he ovat jo sitoutettuja ja lisäys osakkeisiin on vaan kivaa lisää. Niistä ei ole mitään hyötyä muille omistajille. Kuinkakohan monta pientä firmaa löytyy pörssistä joiden johto haluaa suuria optioita itselleen ja tuhoaa tällä tavalla piensijoittajien tuotot? Toki yhtiökokous näistä päättää, mutta näen tässä pukki kaalimaan vartiana tilanteen.
Olenko turhaan huolissani kun tästä ei oikein löydy keskustelua? Tulkitsenko tilanteen täysin väärin?
Niin siis pointtini oli se että nuo kaikki strategiat ovat lopulta plus ja miinus laskuja painotetuista put ja call optioista. Tuo laajennus mihin tahansa funktioon oli lähinnä kuriositeetti siitä että tämä pätee itse asiassa mille tahansa payoff funktiolle h. Esim iron condor strategia on summa yhden ostetun put option payoffista, yhden myydyn putin ja yhden myydyn call option payofista. Tuo voidaan laajentaa myös niin sanotusti sileisiin payoff funktioihin kaavalla
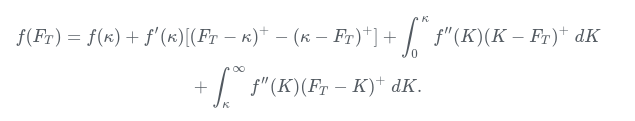
Olettamalla konveksisuuden saadaan tuo vielä yleistettyä vain oikealta striken suhteen jatkuviin payoffeihin (esimerkiksi digitaalinen optio on tällainen).
Sinänsä vaikka voi kuulostaa akateemiselta pölinältä tämä minun sivuseikkani niin sinänsä good to know jos treidaa VIXiä. VIX indeksi nimittäin lasketaan SPX optioiden hinnoista hyödyntäen diskretisoitua erityistapausta tuosta yllä olevasta kaavasta. Sivulla 5 alla olevassa.